What Is Cross-Platform Software Development?
Cross‑platform software development is a methodology for creating applications that can run across multiple operating systems (OS) and devices—such as iOS, Android, Windows, macOS, and Linux—without the need for separate codebases for each.
Leveraging modern frameworks and development tools, teams can craft unified code that adapts to different platforms, preserving performance, user experience, and brand consistency. This approach, often referred to as multi‑platform development, allows organizations to streamline their development process while maintaining a consistent application look and feel.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of cross‑platform development: what it is, how it differs from native approaches, why it’s so popular for mobile, desktop, and web applications, the frameworks developers rely on, and the best practices that can help ensure a robust multi‑platform experience.
Table of Contents
- Defining Cross‑Platform Development
- Why Cross‑Platform Software Matters
- Key Approaches to Cross‑Platform Development
- Popular Frameworks and Tools
- Pros and Cons of Cross‑Platform Development
- When to Choose Cross‑Platform Over Native
- Best Practices for Cross‑Platform Software
- Case Studies and Use Cases
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion

Defining Cross‑Platform Development
Cross‑platform development enables a single codebase to serve multiple operating systems and device types. This unified approach minimizes redundancy and reduces development time by eliminating the need for separate native applications for each platform. By leveraging abstraction layers and modern development tools, developers can write code once and deploy it across mobile, desktop, and web environments. This methodology not only preserves performance but also maintains a consistent user experience and brand identity.
Key aspects of cross‑platform development include the use of frameworks that provide built‑in support for different OS-level APIs and design guidelines. This enables teams to manage code efficiently and update features simultaneously across platforms. The strategic integration of NLP and LSI techniques ensures that related terms like “unified codebase,” “multi‑platform development,” and “native app alternatives” appear naturally within the text.

Why Cross‑Platform Software Matters?
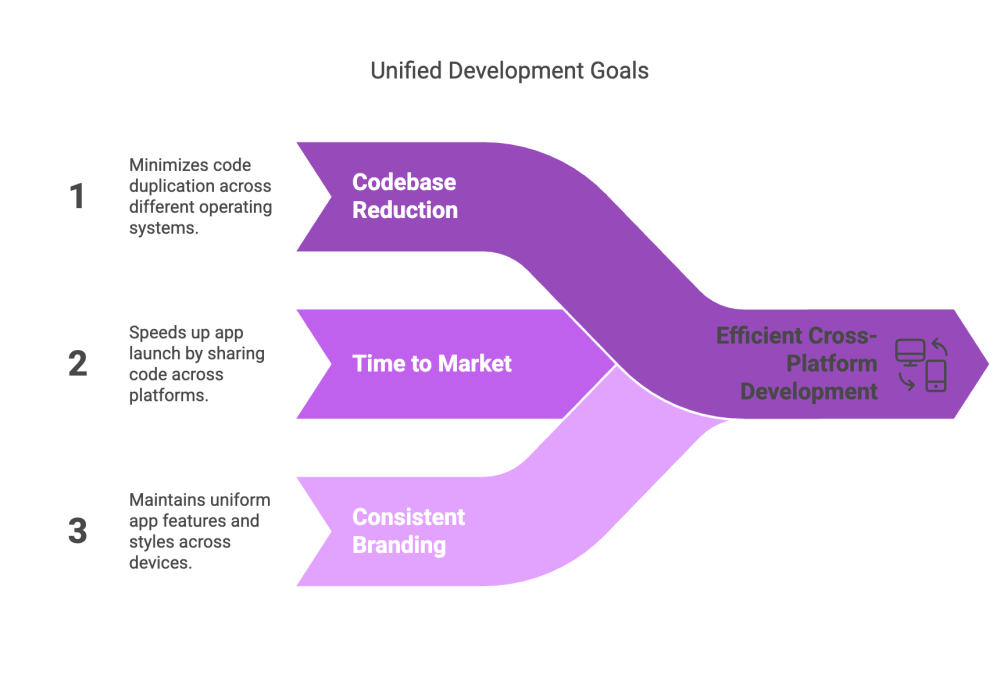
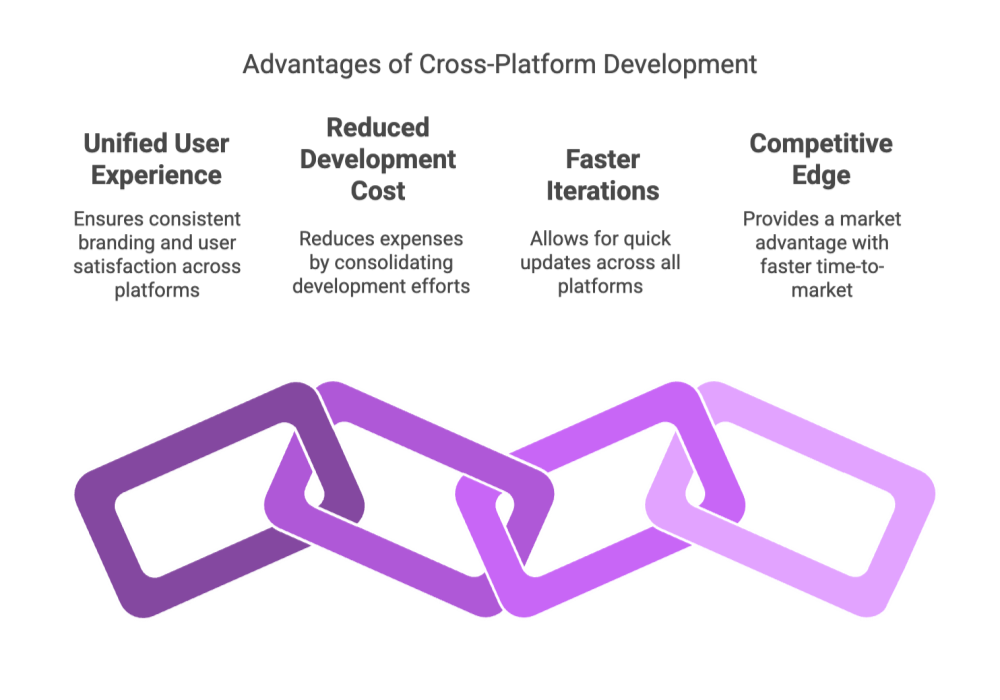
In today’s fragmented device ecosystem, ensuring a unified user experience is critical for maintaining brand consistency and customer satisfaction. Cross‑platform software development allows companies to reach a broader audience by deploying the same application across multiple platforms without sacrificing performance.
This approach also reduces development and maintenance costs, as a shared codebase streamlines updates and bug fixes.
Moreover, the flexibility inherent in cross‑platform development means that teams can iterate quickly and implement new features across all devices simultaneously.

Key Approaches to Cross‑Platform Development
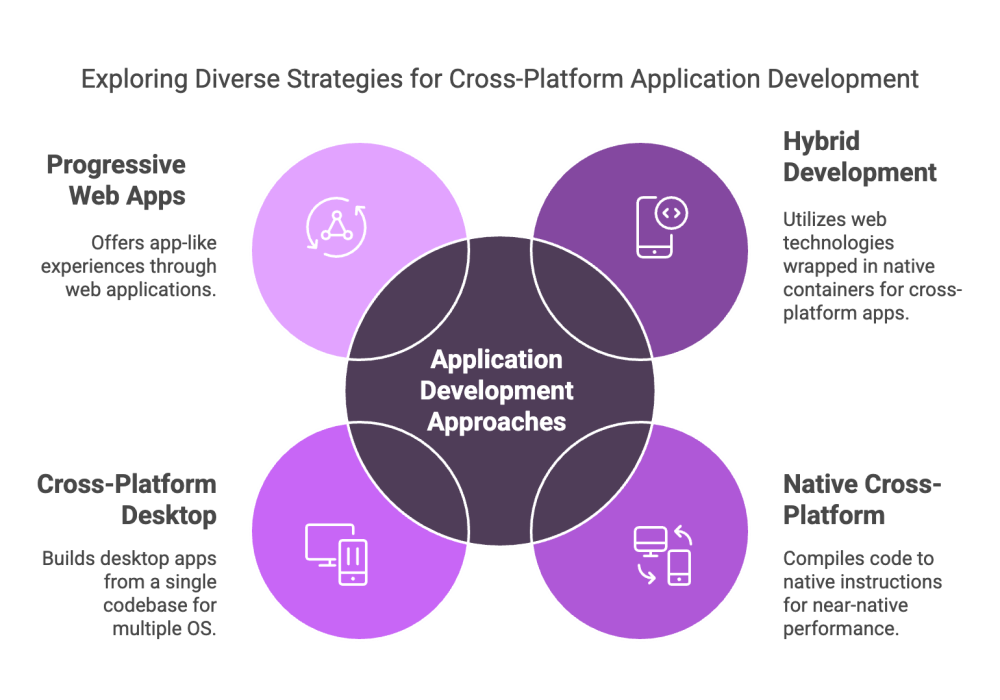
There are several methodologies for cross‑platform development, each with its own benefits and considerations. Two common approaches include:
Hybrid Development
Hybrid development leverages web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) wrapped in a native container to create apps that run on multiple platforms. This method is particularly useful for rapid prototyping and projects with limited budgets. However, it may sometimes face performance challenges compared to native solutions.
Native Cross-Platform Development
Native cross‑platform tools, such as React Native, Flutter, or Xamarin, compile code to native binaries for each platform. This approach delivers performance and UI consistency close to that of purely native apps while still allowing a significant portion of code reuse. It strikes a balance between speed and quality by providing near‑native performance with a shared codebase.

Popular Frameworks and Tools
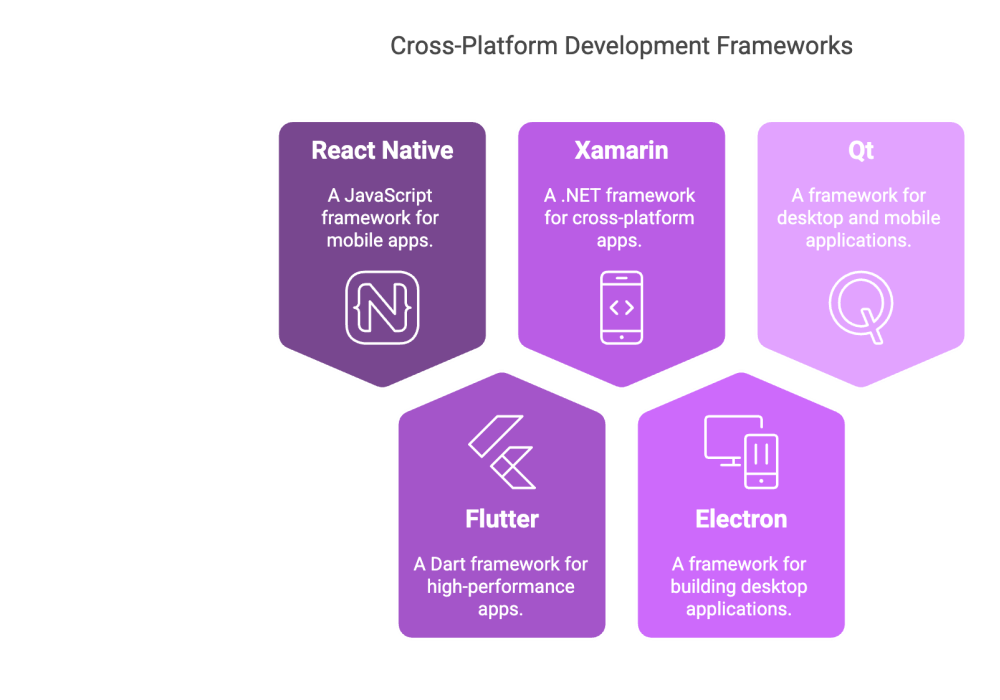
Several frameworks and tools dominate the cross‑platform development landscape, each offering unique advantages. Developers often choose from the following:
- React Native: An open‑source framework that allows for building mobile apps using JavaScript and React. It provides a near‑native look and feel.
- Flutter: Developed by Google, Flutter uses the Dart language to compile applications directly to native code, ensuring high performance and visually appealing UIs.
- Xamarin: A Microsoft‑supported framework that enables developers to build native apps for iOS and Android using C# and .NET.
- Electron: Popular for cross‑platform desktop applications, Electron allows developers to use web technologies to build apps that run on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Qt: A robust framework primarily for desktop applications, offering extensive support for C++ and QML to build cross‑platform software with a native look.
These tools empower teams to maintain a consistent development strategy across platforms while ensuring that applications perform optimally and adhere to native design principles.

Pros and Cons of Cross‑Platform Development
Adopting cross‑platform software development comes with several benefits as well as trade‑offs. Here are some of the key points:
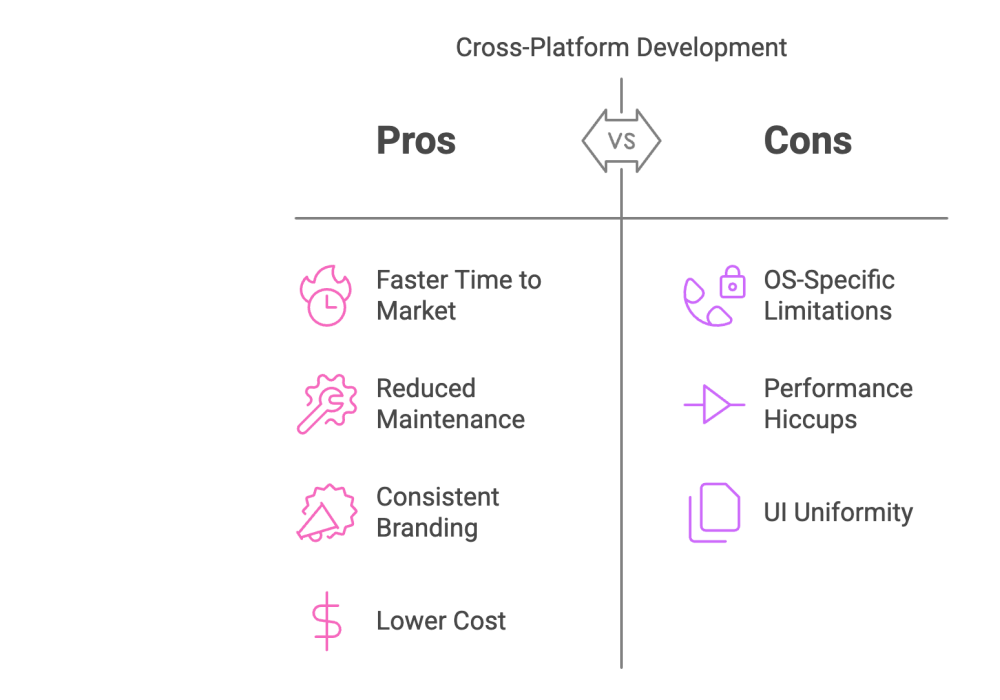
- Pros:
- Faster Time to Market: Reusing a single codebase across multiple platforms accelerates development cycles.
- Reduced Maintenance: With one codebase, updates and bug fixes are implemented uniformly across all platforms.
- Consistent Branding: A unified codebase ensures the same features and design language across different devices.
- Lower Cost: Fewer development resources are required compared to maintaining separate native teams.
- Cons:
- OS‑Specific Limitations: Some frameworks may lag behind in supporting the latest OS features or hardware optimizations.
- Performance Hiccups: Although frameworks like Flutter and React Native approach native performance, highly intensive tasks might perform better with native code.
- UI Uniformity Challenges: Adapting designs to respect individual OS conventions might require additional effort.

'
When to Choose Cross‑Platform Over Native?
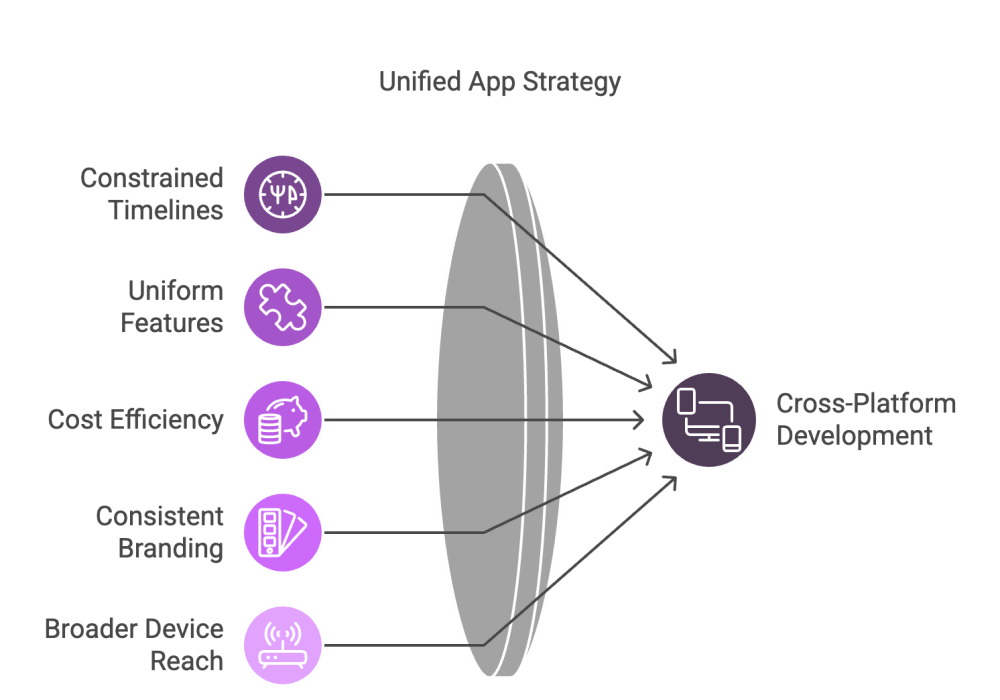
While native development may offer optimal performance and access to the latest OS‑specific features, cross‑platform development is an attractive choice when:
- Constrained Timelines: You need simultaneous releases across multiple platforms.
- Simpler or Uniform Features: Your app’s core logic is largely similar across devices, allowing for efficient code reuse.
- Cost Efficiency: Operating a single development team is often less expensive than managing separate teams for each OS.
- Consistent Branding: A unified codebase simplifies maintaining a consistent user experience and visual identity across platforms.
- Broader Device Reach: Early-stage companies can quickly expand to various platforms without significant additional overhead.

Best Practices for Cross‑Platform Software
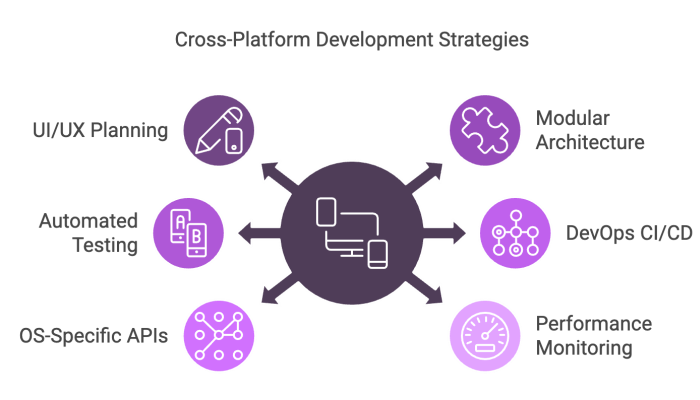
To achieve a robust multi‑platform application, consider the following best practices:
- Plan UI/UX Thoroughly: Decide whether to maintain a uniform experience across all platforms or adapt to each platform’s native design guidelines. Use UI theming to accommodate these variations.
- Adopt a Modular Architecture: Separate core business logic from platform‑specific code. This modularity allows for easier updates and the integration of OS‑specific features through bridging layers.
- Automate Testing: Implement comprehensive testing strategies (unit, integration, UI tests) across different devices and OS environments to ensure consistent performance and compatibility.
- Use DevOps CI/CD Pipelines: Continuous integration and delivery help quickly identify and resolve issues specific to each platform.
- Monitor Performance: Leverage tools to track memory usage, CPU load, and other performance metrics across platforms, ensuring a smooth user experience.

Case Studies and Use Cases
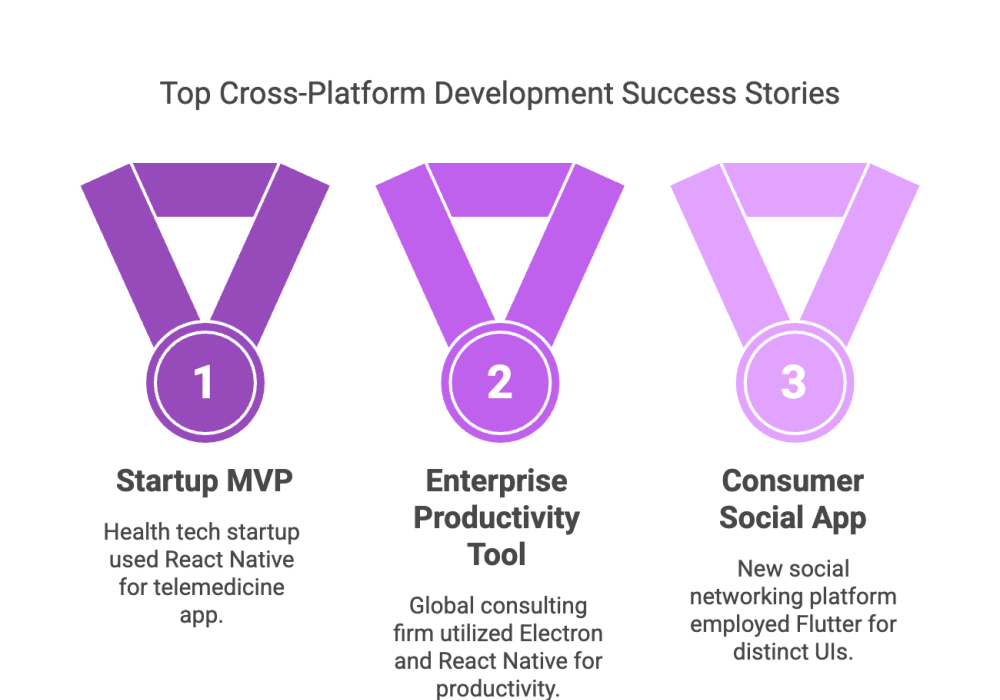
Real-world examples demonstrate the transformative impact of cross‑platform software development:
- Startup MVP: A health‑tech startup used React Native to develop a telemedicine app that worked seamlessly on both iOS and Android, allowing them to launch quickly and gather user feedback.
- Enterprise Productivity Tool: A global consulting firm leveraged Electron for desktop applications and React Native for mobile, achieving consistent functionality and design across all platforms.
- Consumer Social App: A social networking platform used Flutter to deliver a high‑performance mobile experience that translated well to web expansions, ensuring a unified experience for all users.

Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some common questions regarding cross‑platform software development:
- What Is Cross‑Platform Software Development? – It is a development approach that uses a single codebase to create applications for multiple operating systems and devices, reducing duplication and speeding up time to market.
- Does Cross‑Platform Development Mean Less Performance? – Modern frameworks such as Flutter and React Native provide near‑native performance for most applications, though highly specialized or graphics‑intensive tasks may still benefit from native development.
- How Do I Choose the Right Framework? – The choice depends on your project’s scope, your team’s expertise, and performance or UI requirements. Consider factors like community support, learning curve, and integration capabilities.
- Are Cross‑Platform Apps Harder to Maintain? – Generally, maintenance is simplified by having one codebase, although staying current with OS updates and framework versions requires ongoing attention.
- When Should I Opt for Native Development Instead? – If your app demands highly specialized OS-level features, advanced hardware interactions, or extreme performance optimization, native development may be the better option.


Conclusion
Cross‑platform software development is the art and science of building robust applications that deliver a consistent user experience across multiple operating systems and devices—all from a single codebase. In 2025, this approach has become essential for startups and enterprises alike, enabling rapid deployment, cost‑effective maintenance, and agile adaptation to evolving market demands.
By selecting the right framework, adopting best practices, and leveraging modern tools, organizations can harness the power of cross‑platform development to accelerate innovation and maximize ROI. Whether you choose to use React Native, Flutter, Electron, or a combination of technologies, the goal remains the same: to create applications that are not only efficient and scalable but also provide a seamless, engaging experience for users worldwide.

Let's connect!
If you’re ready to harness the power of cross‑platform software development to build scalable, user‑centric applications, contact us today. Our team of experts is here to guide you through every step of your multi‑platform journey, ensuring that your solutions are robust, future‑proof, and aligned with your business objectives.

